Argyll and Bute
All of our services are available on self-referral and are confidential. We will never share your information without your consent. Choose from the options below to find out more about the services we offer.
HIV and syphilis testing
Our rapid HIV and syphilis testing is completely free and confidential.
One to one support
Our one to one support services are designed to provide a safe and welcoming environment where you can talk openly without judgement or stigma.
Peer support
Living with HIV can affect just about every aspect of your life. Sometimes it’s good to talk to someone who can relate.
Support for gay and bisexual men
Our service for gay, bisexual and all men who have sex with men offers advice and support around sexual health, whether you are living with HIV or not.
Free condoms by post
If you live in Argyll and Bute, we can send you free condoms and lubricant. Using condoms and lubricant can help prevent HIV and other sexually transmitted infections.
Free infant formula milk programme
Our free infant formula milk programme is available to all new or expecting parents living with HIV in Argyll and Bute.
Sexual health services from GP surgeries
GP practices are able to provide routine contraception, tests and treatment for common sexually transmitted infections and cervical smear tests. Many GPs also provide coils, implants and able to supply free condoms.
Professional training
Our training sessions are highly evaluated and run throughout the year both online and in person for those working in Argyll and Bute.
Other sexual health services
Other NHS sexual health services in nearby areas
Rapid testing
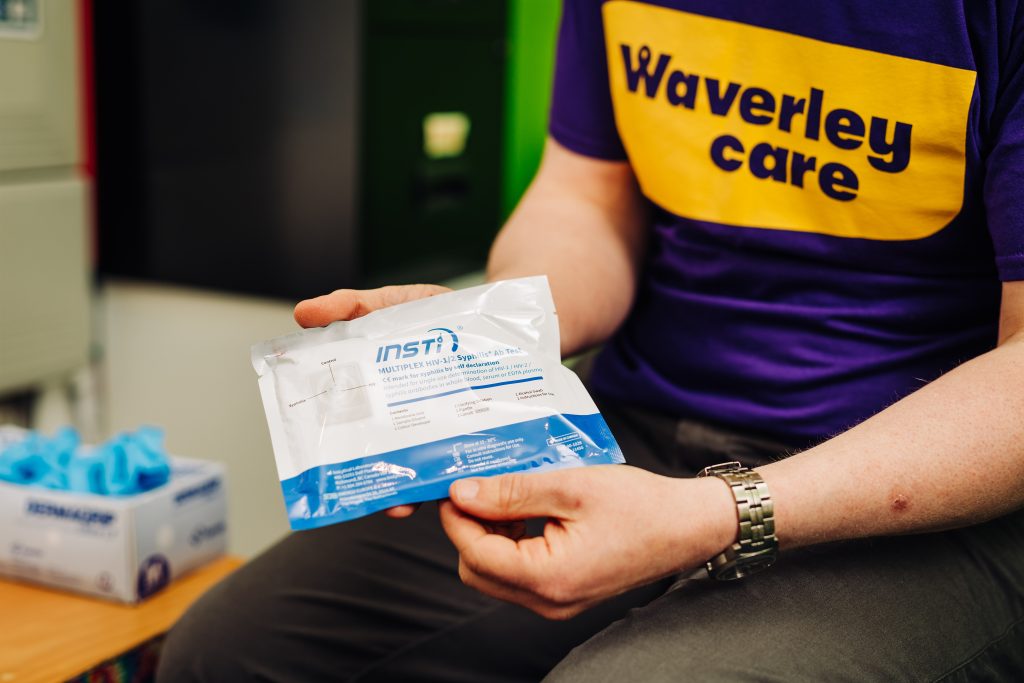
Rapid testing is a quick and easy way to test for HIV and syphilis. It is confidential and completely free of charge.
We can offer testing to anyone aged 18+ and we can usually arrange testing appointments anywhere in Argyll and Bute or can discuss alternatives like home testing.
Book Now
What you can expect
You might feel a bit nervous about having a test, especially if it’s your first one. Rest assured, the process is straightforward and our staff are trained to make you feel at ease. They are also there to answer any questions you may have.
Read more about rapid HIV and syphilis testing at Waverley Care.
Test yourself for HIV
HIV self tests are fast and totally confidential. You can order free and low-cost blood and oral HIV testing kits from the charity Terrence Higgins Trust.
Back to top
One to one support
If you are living with HIV and need support, our Health Improvement Coordinators can work with you to develop a support plan to best meet your needs.
Our services are completely confidential and flexible to your needs. We can arrange an appointment over the phone, online or meet you somewhere that is comfortable for you.
What to expect
One to one support can help you with:
- Coping with a new diagnosis,
- Understanding and accessing treatment,
- Improving mental health and wellbeing,
- Attending appointments and talking to your doctor,
- Telling your family, friends or colleagues about your HIV status.
As well as offering emotional support, our Health Improvement Coordinators can offer practical support like attending medical appointments and can signpost to other organisations that may be able to help with a specific issue, such as homelessness or support accessing benefits.
Get support
Back to topPeer support
At Waverley Care, we can put you in touch with one of our trained peer mentors who have lived experience of HIV and can help you work through some of the challenges you may be facing in your day-to-day life.
What to expect
If you need support with HIV, peer support can help you in a variety of ways including:
- Thinking positively about the future,
- Disclosing your HIV status to family, friends and others,
- Increasing your confidence and self-esteem,
- Feeling less isolated,
- Living well with HIV and managing treatment.
If you would like to access peer support or become a peer mentor, get in touch.
Get in touch
Back to topSex, health and wellbeing
We offer support to all gay and bisexual men, and all men who have sex with men who want to develop the knowledge, skills and confidence to take control of and make informed decisions about their sexual health.
We promise you a welcoming, confidential and supportive service, free from judgement and discrimination. Our Health Improvement Coordinators are well equipped to support individuals who face discrimination because of their identity, sexuality, gender, sexual health or HIV status.
Who is this service for
This service is for anyone who identifies as a gay or bisexual man. This includes trans men, non-binary or gender-fluid people who want to access spaces for men. This service is also open to men who have sexual and/or romantic relationships with other men, but do not identify as gay or bisexual.
What support we offer
We offer one to one support where you can speak to one of our Health Improvement Coordinators about your sexual health and wellbeing in a confidential and non-judgmental space.
One to one support is tailored to your needs and can be provided in person or online. We can discuss a broad range of topics, including:
- Sex, relationships and sexual health,
- HIV and other sexually transmitted infections,
- Coming to terms with your sexuality,
- Coming out,
- Making social connections within the LGBTQ+ community,
- Reporting hate crime.
We also run clinics in community venues across Scotland, offering rapid HIV and syphilis testing as well as advice and education about HIV and sexual health.
Peer support
We want to provide opportunities for gay, bisexual and men who have sex with men to meet up, socialise and get support from each other in a confidential, relaxed setting. We can put you in touch with our trained peer mentors who have lived experience of HIV and can help you work through some of the challenges you may be facing in your day-to-day life, either one to one or as part of a group.
Get support
Back to topCondoms by Post scheme
You can order condoms and lubricant online using our online order form. Materials are posted in plain packaging to maintain confidentiality and you can make an order request every 3 months.
Our orders are processed fortnightly but if you need condoms more urgently, you can collect condoms from our Inverness office at 6 Ardross Street. Let us know you’re coming in by calling 01463 711585 or emailing argyllandbute@waverleycare.org.
For more information, and for condoms by post schemes in other areas, click the button below.
Get free condoms by post
Under 25?
If you are under 25, please order condoms through this form.
Back to top
Free infant formula milk
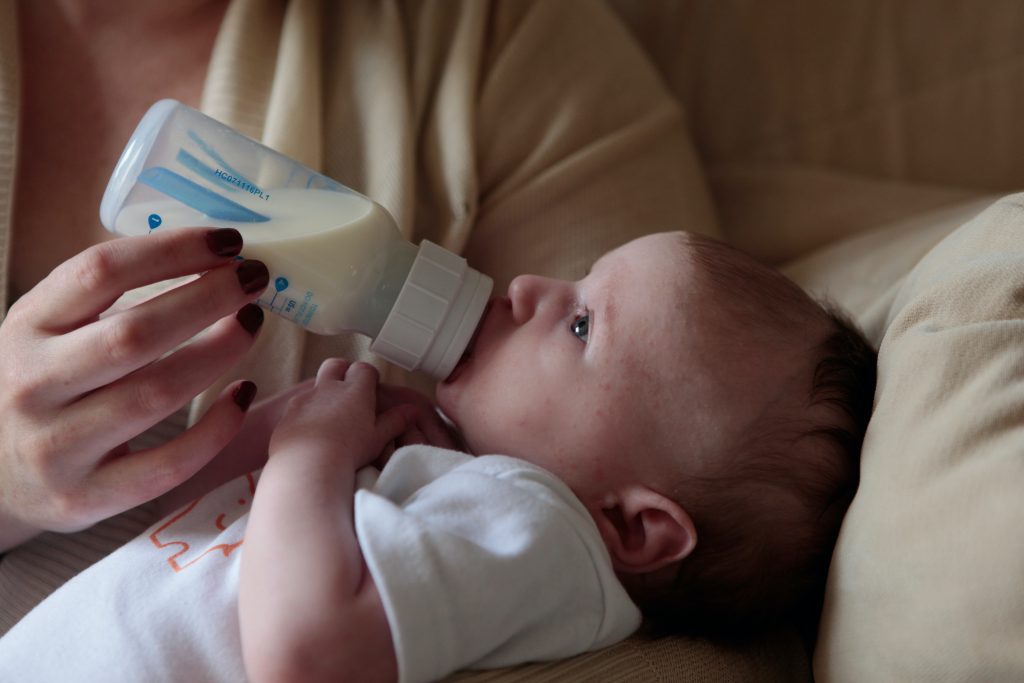

To prevent the transmission of HIV to newborn babies, official guidelines recommend that people living with HIV do not breast/chestfeed and instead exclusively formula feed their babies.
However, formula milk is an expensive option that some parents struggle to afford. Commonly available powdered formulas can cost anything from £30-£60 per month depending on the brand and that’s before you factor in the additional costs of bottles and sterilisers.
To overcome this barrier, Waverley Care can provide free formula milk for babies from birth up to age one.
We provide
- 4 tins of formula a month for the first year of baby’s life,
- Free bottles and sterilising equipment,
- Flexible collection and delivery options,
- Free and confidential support services.
How to access
If you are living with HIV and are pregnant, speak to your HIV specialist nurse about a referral or get in touch with us for information and advice.
Get in touch
Back to topSpecialised GP Practices
There are three GP practices that provide more specialised services and are available to anyone, you do not need to be registered with these practices to get an appointment. Practitioners at these services will have a specialist training in this area of work.
Lorn Medical Centre (Oban)
Tel 01631 563 175
Lochgilphead Medical Centre
Tel 01546 462 002
Campbeltown Medical Practice
Tel 01586 552 105
Back to topSexual Health Key Messages
This session is a fantastic starting point for a variety of professionals working in education, health, and third sector/voluntary organisations. Working well as both a beginner’s guide, or a refresher of key information, the session covers:
- Condoms; why use them, how to use them, and where to get them
- Sexually Transmitted Infections, Blood Borne Viruses, testing, and stigma
- Contraception; options and access
- Communicating with Service Users
This session is generally 2.5 hours long.
For a more in depth understanding, it can be combined into a longer session with HIV & Hepatitis Awareness or Working With Young People: Sex & Relationships.
Next session: Next session to be announced soon, please check again later or get in contact with us
Time: TBA
Location: TBA
HIV & Hepatitis Awareness
This session provides an understanding of Blood Borne Viruses (HIV, Hep C and Hep B) and how they affect the people who live with them. We will cover the following:
- Explanation of HIV and Hepatitis B & C, including transmission and treatment
- The social impacts of living with a Blood Borne Virus including stigma and discrimination
- Working with service users to reduce harm – including through prevention and testing
- Support services and signposting
This session is generally 2 hours long. Additional content on condom use can be integrated for a longer session.
Next session: Wednesday 6th March 2024
Time: 10am
Location: Ardross Street, Inverness
Working With Young People: Sex & Relationships
This session will provide an increased confidence for professionals working with young people in addressing issues and exploring attitudes around sexual behaviour and relationships. We will cover the following:
- The experiences young people have today, and what influences them, regarding their sexual health & relationships
- Barriers, issues, and worries that young people face when talking to professionals or accessing services
- Barriers, issues, and worries that we may have as practitioners
- How to address these barriers and communicate in a positive, inclusive, and safe way
This session is generally 3 hours long, with multiple options for tailored content.
It works well combined into a full day session with Sexual Health Key Messages, or can be supplemented with additional content on Sex & The Law, or LGBTQ+ Young People’s Sexual Health.
Team Talks
Do you have a spare slot in your team meeting, and want to find out more about the work of Waverley Care and Wave Highland? We are happy to come along to discuss our service and answer any questions.
To Book
Training runs throughout the year online, and at rotational sites throughout Highland, Argyll, and Bute.
You can book via Eventbrite here.
Alternatively, to discuss specific training for your organisation, or if you would like to combine options and create a bespoke session, please contact hello@wavehighland.com.
You may also join our newsletter here to be informed of future training dates.
Back to top
Fort William
Belford Hospital Fort William
Sexual and Reproductive Health Care Clinic Every Thursday – please phone for an appointment.
Psycho-sexual counselling 2nd and 4th Thursday each month 18.00-20.00.
Tel. 01397 707406 / 01463 888300
Oban
Market Street Centre
Market Street
Oban
PA34 4HR
- Sexual Health advice and screenings for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and blood borne viruses (BBV) available
- Information and referral for PrEP
Appointments only, please call: 07900 136571
Back to top